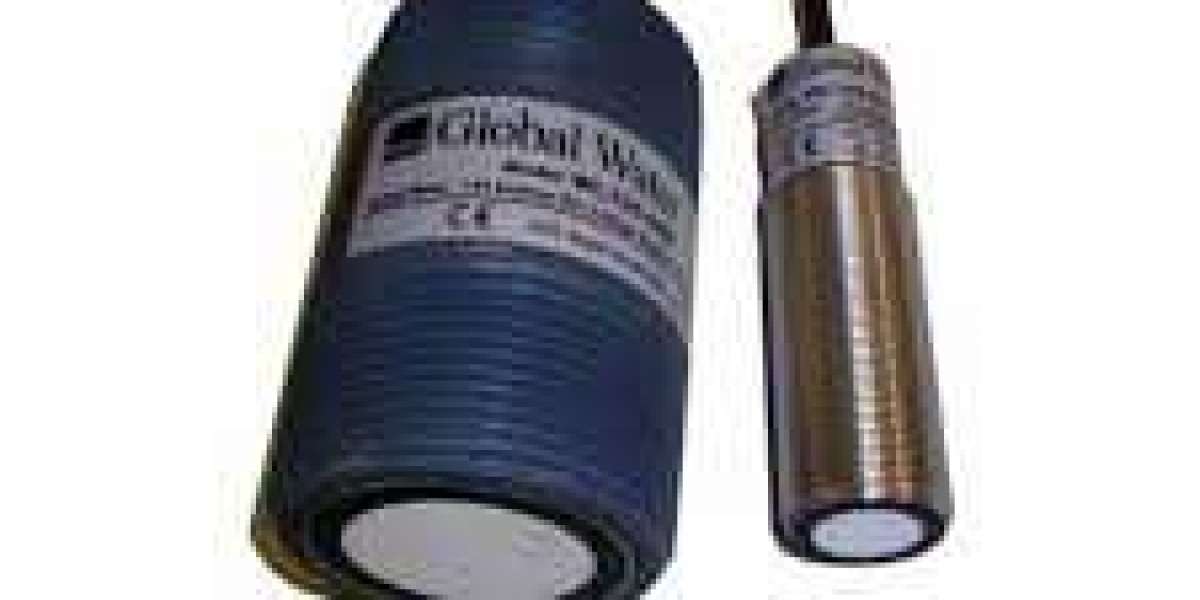
An ultrasonic level transmitter is a device used to measure the level of a liquid or solid substance in a container or tank using ultrasonic waves. It works based on the principle of sound waves and their reflection.
The basic components of an ultrasonic level transmitter include a transducer, which emits and receives ultrasonic waves, and an electronic circuitry that processes the received signals. The transducer typically consists of a piezoelectric crystal that converts electrical energy into ultrasonic waves and vice versa.
The working principle of an ultrasonic level transmitter involves the following steps:
Generation of Ultrasonic Waves: The transmitter generates high-frequency ultrasonic waves typically in the range of 20 to 200 kHz. These waves are produced by applying an electric current to the piezoelectric crystal in the transducer, causing it to vibrate at the desired frequency.
Emission of Ultrasonic Waves: The transducer emits the generated ultrasonic waves into the medium, usually air or a process material. The waves propagate through the medium at a known speed, which is determined by the characteristics of the medium.
Reflection of Ultrasonic Waves: When the ultrasonic waves encounter the surface of the substance being measured, they get partially reflected back toward the transducer. The extent of reflection depends on the density and acoustic properties of the material.
Reception of Reflected Waves: The transducer acts as a receiver and picks up the reflected ultrasonic waves. The reflected waves carry information about the distance between the transducer and the material's surface. The transducer converts the received ultrasonic transmitter into electrical signals.
Time-of-Flight Measurement: The electronic circuitry measures the time taken for the ultrasonic waves to travel from the transducer to the material's surface and back. This is known as the time-of-flight measurement. The circuitry uses a timing mechanism, such as a counter or a microprocessor, to accurately measure the time.
Calculation of Level: Using the known speed of sound in the medium and the measured time-of-flight, the transmitter calculates the distance between the transducer and the material's surface. This distance corresponds to the level of the substance in the tank or container.
Output Display or Transmission: The calculated level measurement is displayed on the transmitter's interface, which can be a digital screen or an analog indicator. Additionally, the transmitter may also provide an output signal, such as a 4-20 mA current loop or a digital communication protocol, to transmit the level information to a control system or data acquisition device.
It is worth mentioning that ultrasonic level transmitters can employ different techniques to enhance accuracy and overcome challenges like turbulence, foam, or varying material properties. These techniques may include signal filtering, temperature compensation, multiple transducers for redundancy, and advanced algorithms for data processing.
In summary, ultrasonic level transmitters utilize ultrasonic waves to measure the distance between the transducer and the material's surface, allowing for accurate level measurements in various industrial applications. The generation, emission, reflection, and reception of ultrasonic waves, along with precise time-of-flight measurement and calculations, enable these devices to provide reliable and real-time level information